Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Training and Development in HRM
Training and development in HRM (Human Resource Management) are crucial processes that enhance the capabilities of employees, ensuring that they remain competent and competitive in their roles. These processes involve systematic procedures aimed at improving the skills, knowledge, and behaviors of employees to align with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!What is Training and Development in HRM?
To understand what training and development in HRM entail, it’s essential to distinguish between the two: Training refers to the process where employees are taught specific skills or knowledge to improve their current job performance. It is typically short-term and focuses on the immediate needs of the job. Development, on the other hand, is a long-term process aimed at the overall growth of the employee. It prepares employees for future roles and responsibilities, fostering personal and professional growth. Understanding the difference between training and development in HRM is critical for HR professionals to design effective programs that meet both the immediate and future needs of their organizations.
Benefits of Training and Development in HRM
Enhancing Employee Performance – One of the primary benefits of training and development in HRM is the enhancement of employee performance. For example, a sales team trained in the latest customer relationship management (CRM) software can improve sales efficiency and customer satisfaction. Training programs tailored to specific job roles ensure that employees have the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their duties effectively, leading to higher productivity and better job performance.
Boosting Employee Morale and Job Satisfaction – Investing in employee development fosters a sense of value and belonging among staff. When employees see that the company is willing to invest in their growth, they are more likely to feel appreciated and motivated.
Ensuring Adaptability to Industry Changes – The importance of training and development in HRM is particularly evident in industries that experience rapid technological advancements. Continuous training helps employees stay updated with the latest trends and technologies.
Reducing Employee Turnover – Organizations that prioritize training and development often experience lower turnover rates. When employees feel that they are growing and advancing within the company, they are less likely to seek opportunities elsewhere
Improving Organizational Competitiveness Through effective training and development, organizations can enhance their overall competitiveness. Employees equipped with the latest skills and knowledge can contribute to innovative solutions and improved processes.
Facilitating Management Development in Human Resource Management – Training HRM professionals and developing management capabilities is crucial for the overall health of an organization. Programs focused on management development in human resource management ensure that future leaders are prepared to take on more significant responsibilities.The purpose is to deliver theoretical knowledge and practical skills through interactive and structured learning.
Types of Training Methods in HRM
- On-the-Job Training (OJT)
- Definition: On-the-job training (OJT) involves employees learning job tasks while performing them under the supervision and guidance of experienced workers.
- Purpose: The purpose of OJT is to equip employees with the skills and knowledge necessary for their specific job roles by exposing them to real work situations.
- Key steps involved in implementation:
- Preparation: Identify the skills required for the job and select experienced employees as trainers.
- Demonstration: Trainers demonstrate the tasks and explain each step involved.
- Practice: Trainees perform the tasks under supervision, with immediate feedback and corrections.
- Follow-Up: Monitor the trainee’s progress and provide additional support as needed.
- Example: In a retail setting, a new cashier can be trained on the job by an experienced cashier. The trainer demonstrates how to use the cash register, handle transactions, and provide customer service. The trainee then practices these tasks while the trainer observes and offers guidance.
- Mentorship and Coaching
-
- Definition: Mentorship and coaching involve experienced employees (mentors or coaches) guiding less experienced employees (mentees or coachees) through regular interactions and feedback.
- Purpose: The purpose is to develop the mentee’s skills, knowledge, and professional growth through personalized support and advice.
- Key steps involved in implementation:
- Pairing: Match mentors with mentees based on skills, goals, and compatibility.
- Goal Setting: Establish clear objectives and expectations for the mentorship or coaching relationship.
- Regular Meetings: Schedule regular sessions for guidance, feedback, and progress reviews.
- Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of the mentorship or coaching relationship and make adjustments as needed.
- Example: A new marketing manager may be paired with a senior marketing executive. They meet bi-weekly to discuss
strategies, review performance, and address challenges, helping the new manager develop strategic thinking and leadership skills.
- Job Rotation
- Definition: Job rotation involves employees moving between different roles or departments within the organization to gain a broad understanding of various functions.
- Purpose: The purpose is to develop a versatile workforce with diverse skills and knowledge, preparing employees for future leadership roles.
- Key steps involved in implementation:
- Planning: Identify the roles and departments suitable for rotation and create a rotation schedule.
- Orientation: Provide orientation and training for each new role.
- Rotation: Implement the rotation plan, allowing employees to spend designated time in each role.
- Feedback: Collect feedback from employees and managers to assess the rotation’s effectiveness.
- Example: In a manufacturing company, an engineer might rotate between production, quality control, and maintenance departments, gaining insights into different aspects of the manufacturing process.
- Classroom Training
- Definition: Classroom training involves structured learning sessions conducted by trainers in a classroom setting.
- Purpose: The purpose is to deliver theoretical knowledge and practical skills through interactive and structured learning.
- Key steps involved in implementation:
- Needs Assessment: Determine the training needs and objectives.
- Curriculum Development: Develop a curriculum and training materials.
- Scheduling: Plan and schedule the training sessions.
- Delivery: Conduct the training sessions, incorporating interactive activities and discussions.
- Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of the training through tests, feedback, and performance assessments.
- Example: A financial services firm might conduct classroom training for new hires on regulatory compliance, covering topics such as anti-money laundering (AML) laws and ethical standards.
- E-Learning and Online Training
- Definition: E-learning and online training involve using digital platforms and resources to deliver training programs.
- Purpose: The purpose is to provide flexible, accessible, and cost-effective training that can be accessed anytime and anywhere.
- Key steps involved in implementation:
- Platform Selection: Choose a suitable e-learning platform or Learning Management System (LMS).
- Content Development: Create or curate engaging and interactive online training content.
- Implementation: Launch the training program on the platform.
- Monitoring and Support: Track progress and provide support and feedback as needed.
- Example: A global IT company might use an online platform to deliver cybersecurity training to employees worldwide, incorporating videos, quizzes, and interactive modules.
- Workshops and Seminars
- Definition: Workshops and seminars are intensive training sessions focusing on specific skills or knowledge areas.
- Purpose: The purpose is to provide in-depth learning on particular topics through interactive and practical sessions.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Topic Selection: Identify the specific skills or knowledge areas to be addressed.
- Expert Facilitation: Engage subject matter experts to conduct the sessions.
- Interactive Activities: Incorporate hands-on activities, discussions, and group work.
- Feedback and Follow-Up: Collect feedback and provide follow-up resources or support.
- Example: A pharmaceutical company might organize a workshop on the latest developments in drug formulation techniques, featuring expert speakers and practical lab sessions.
- Certification Programs
- Definition: Certification programs are specialized training programs that lead to professional certifications recognized within the industry.
- Purpose: The purpose is to validate employees’ skills and knowledge, enhancing their professional credibility and career prospects.
- Key steps involved in implementation:
- Program Selection: Identify relevant certification programs based on industry standards.
- Preparation: Provide study materials and resources to prepare for certification exams.
- Enrollment: Register employees for the certification programs.
- Support: Offer support and resources throughout the certification process.
- Example: An HR professional might pursue a certification program like the Professional in Human Resources (PHR) to demonstrate expertise and advance their career.
- Blended Learning
-
- Definition: Blended learning combines traditional classroom training with online learning to create a comprehensive training experience.
- Purpose: The purpose is to leverage the strengths of both in-person and online training methods to provide a well-rounded learning experience.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Design: Develop a blended learning curriculum that integrates classroom and online components.
- Implementation: Schedule and deliver the classroom sessions and online modules.
- Interaction: Facilitate interaction and engagement through discussions and activities.
- Assessment: Evaluate learning outcomes through tests, assignments, and feedback.
- Example: A healthcare organization might use blended learning for medical training, combining online modules on theoretical concepts with hands-on practice in a classroom or clinical setting.
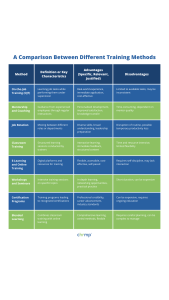
These methods cover a wide range of approaches, catering to different learning needs and organizational contexts, thereby providing a robust framework for training and development in HRM.
Steps to Implement Effective Training Programs in HRM
Implementing effective training programs is a critical aspect of training and development in HRM. A well-structured process ensures that training initiatives meet organizational goals and enhance employee performance. This section outlines the key steps involved in creating successful training programs, integrating relevant HRM keywords for a comprehensive understanding.
- Conducting Needs Assessment
- Definition: A needs assessment identifies the skills, knowledge, and abilities that employees need to improve their performance and align with organizational objectives.
- Purpose: The purpose is to ensure that the training program addresses the actual needs of the organization and its employees, rather than perceived needs.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Identify Objectives: Clarify what the organization aims to achieve with the training.
- Collect Data: Use surveys, interviews, performance appraisals, and job analysis to gather information.
- Analyze Data: Identify gaps between current competencies and required skills.
- Prioritize Needs: Determine which training needs are most critical and should be addressed first.
- Example: A manufacturing company might conduct a needs assessment to determine that employees require updated training on new machinery to improve production efficiency and safety.
- Setting Training Objectives
- Definition: Training objectives are specific, measurable goals that the training program aims to achieve.
- Purpose: The purpose is to provide a clear direction for the training program and establish criteria for evaluating its success.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Define Clear Goals: Establish what the training should accomplish.
- Make Objectives SMART: Ensure objectives are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Align with Business Goals: Ensure that training objectives support broader organizational goals.
- Example: For a customer service training program, an objective might be: “Reduce customer complaint resolution time by 20% within six months.”
- Choosing Appropriate Training Methods
- Definition: Selecting the right training methods involves determining the most effective ways to deliver training content based on the objectives and audience.
- Purpose: The purpose is to choose methods that will most effectively facilitate learning and skill acquisition.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Assess Options: Evaluate different types of training methods in HRM, such as on-the-job training, e-learning, and workshops.
- Consider Audience: Choose methods that match the learning styles and needs of the trainees.
- Evaluate Resources: Consider the availability of time, budget, and training facilities.
- Example: An IT company might choose a blended learning approach for software training, combining online modules with hands-on classroom sessions.
- Developing Engaging Content
- Definition: Creating engaging content involves designing training materials that effectively communicate the necessary information and skills.
- Purpose: The purpose is to ensure that the training content is informative, relevant, and engaging, promoting better learning outcomes.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Content Outline: Develop a detailed outline of the training program.
- Instructional Design: Use principles of instructional design to create interactive and engaging materials.
- Incorporate Multimedia: Use videos, infographics, and other multimedia elements to enhance learning.
- Pilot Testing: Test the content with a small group of employees and gather feedback for improvement.
- Example: For a sales training program, developing interactive role-play scenarios can help employees practice and refine their sales techniques.
- Delivering the Training
- Definition: Delivering the training involves the actual implementation of the training program to the intended audience.
- Purpose: The purpose is to facilitate the transfer of knowledge and skills from the training content to the employees.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Schedule Sessions: Plan the timing and logistics of the training sessions.
- Choose Trainers: Select qualified trainers or facilitators to conduct the sessions.
- Engage Participants: Use interactive techniques to keep participants engaged and motivated.
- Provide Support: Ensure that trainees have access to resources and support during the training.
- Example: A healthcare organization might deliver training through a combination of live webinars and in-person workshops, ensuring flexibility and engagement.
- Evaluating and Gathering Feedback
- Definition: Evaluation and feedback involve assessing the effectiveness of the training program and collecting input from participants.
- Purpose: The purpose is to determine whether the training objectives were met and identify areas for improvement.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Assessment Tools: Use quizzes, tests, and practical assessments to measure learning outcomes.
- Collect Feedback: Gather feedback from participants through surveys and interviews.
- Analyze Results: Evaluate the data to assess the training’s impact on performance and objectives.
- Report Findings: Share the results with stakeholders and make recommendations for improvements.
- Example: After a leadership development program, a company might use 360-degree feedback to assess the effectiveness of the training on leadership behaviors.
- Continuous Improvement of Training Programs
- Definition: Continuous improvement involves regularly updating and enhancing training programs based on feedback and changing needs.
- Purpose: The purpose is to ensure that training programs remain relevant, effective, and aligned with organizational goals.
- Key Steps Involved in Implementation:
- Review Feedback: Continuously review feedback and evaluation results.
- Update Content: Revise training materials to incorporate new information and best practices.
- Adapt Methods: Modify training methods to better suit evolving needs and technologies.
- Monitor Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and incorporate them into training programs.
- Example: A financial services firm might continuously update its compliance training program to reflect new regulations and industry standards.
Conclusion
Effective training and development in HRM are essential for fostering a skilled, motivated, and adaptable workforce. By systematically implementing these processes, organizations can enhance employee performance, boost morale, ensure adaptability to industry changes, reduce turnover, and improve overall competitiveness.
Each method, from on-the-job training to e-learning, offers unique benefits and requires careful consideration and planning to align with organizational goals. Understanding the difference between training and development in HRM is crucial for HR professionals. By conducting a thorough needs assessment, setting clear training objectives, choosing appropriate methods, developing engaging content, delivering training effectively, evaluating results, and continuously improving training programs, HR professionals can ensure that their training initiatives are both effective and impactful.
Investing in management development in human resource management also prepares future leaders, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and growth within the organization. As the HR landscape evolves, staying updated with the latest trends and best practices is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the process of training and development in HRM. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments section below. Your feedback helps us continue to improve and deliver relevant and helpful content. Let’s continue the conversation and learn from each other’s experiences in this vital aspect of HRM.





