Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Behavioral Event Interviewing (BEI) has emerged as a pivotal tool in the recruitment arsenal of modern organizations. As we navigate through 2024, the significance of BEI in hiring the best talent cannot be overstated. This methodology delves deeper than traditional interviews, uncovering the true competencies of candidates through past behavior analysis.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!This blog will explore the nuances of BEI, providing HR professionals with practical insights and actionable strategies to enhance their hiring processes. It is designed to equip HR professionals with the knowledge and tools needed to hire the best talent efficiently and effectively.
The Cost of a Mishire
Financial Impact
Hiring the wrong candidate can be extremely costly for an organization. Studies estimate that the cost of a bad hire can be up to fifteen times the employee’s annual salary, considering recruitment costs, training expenses, lost productivity, and the impact on team morale and company culture.
Impact on Team Morale
Hiring the wrong candidate can also negatively impact team morale and productivity. Team members may become disengaged or frustrated, leading to higher turnover rates and additional recruitment costs.
Reputational Damage
A mishire can damage an organization’s reputation, particularly if the hire is in a customer-facing role. Poor performance can lead to dissatisfied customers and potential damage to the brand’s image.
Common Interview Pitfalls
Bias in Interviewing
Traditional interviewing methods often fall prey to biases, whether conscious or unconscious. Interviewers might favor candidates who share similar backgrounds, experiences, or even personalities, leading to a less diverse and potentially less effective team.
Lack of Structure
Many traditional interviews lack a structured format, leading to inconsistent evaluations. Without a standardized approach, it becomes challenging to compare candidates objectively, increasing the risk of a poor hiring decision.
Overemphasis on Technical Skills
While technical skills are important, overemphasizing them can result in neglecting crucial soft skills and cultural fit. This can lead to hiring technically proficient candidates who might not thrive within the organization’s environment.
Inconsistent Applicant Evaluation
Interviewers often have different benchmarks and evaluation standards, which can result in inconsistent assessments. This randomness across the organization means that selection elements are not organized into a system, affecting the fairness and accuracy of the hiring process.
Relative Quality Bias
Decisions are sometimes affected by the relative quality of other applicants rather than the specific requirements and competencies needed for the job. This can lead to selecting candidates who might not be the best fit for the role.
Poor Note-Taking
Interviewers may take insufficient notes during interviews, leading to poor recall of key points during reviews or debriefs. This can impact the decision-making process and result in suboptimal hiring choices.
Why Behavioral Event Interviewing (BEI) is Superior
Behavioral Event Interviewing addresses these common pitfalls effectively:
- Systematic and Objective Evaluation: BEI ensures that applicant information is discussed systematically and objectively. The structured nature of BEI means that all candidates are evaluated based on the same criteria, reducing bias and ensuring consistency.
- Organized Selection Elements: BEI organizes the selection elements into a coherent system. This structured approach ensures that every interviewer follows the same process, leading to more reliable and valid assessments.
- Consistent Benchmarks: By defining clear competencies and evaluation criteria, BEI ensures that different interviewers have consistent benchmarks and standards, reducing variability in candidate evaluations.
- Focus on Required Competencies: BEI focuses on specific behaviors and competencies required for the job, rather than being influenced by the relative quality of other applicants. This targeted approach helps in identifying the best fit for the role.
- Detailed Note-Taking: The structured format of BEI encourages detailed note-taking, ensuring that key points are recorded and can be reviewed accurately during debriefs.
Understanding Behavioral Event Interviewing (BEI)
Definition and Principles of BEI
Behavioral Event Interviewing is a structured interview technique that focuses on the candidate’s past behavior as a predictor of future performance. Developed in the 1970s by David McClelland, BEI revolves around the premise that past behavior in specific situations is the best indicator of future behavior.
The Best Indicator of Future Behavior is Past Behavior
The fundamental presumption of BEI is that the best predictor of how someone will perform in the future is how they have performed in the past under similar circumstances. For example, if a candidate has successfully led a project under tight deadlines in their previous job, it is likely they will handle similar pressures well in the future. This principle helps employers focus on concrete evidence of a candidate’s capabilities rather than relying on speculative or hypothetical scenarios.
The Evolution of BEI Over the Years
Over the decades, BEI has evolved to become a sophisticated tool used by leading organizations worldwide. Initially focused on executive recruitment, it has now permeated all levels of hiring, ensuring a more comprehensive evaluation of candidates.
The Behavioral Event Interview Process
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the BEI Process
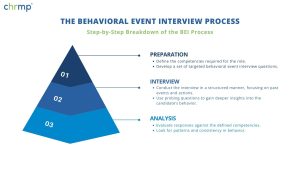
- Preparation:
- Define the competencies required for the role.
- Develop a set of targeted behavioral event interview questions.
- Interview:
- Conduct the interview in a structured manner, focusing on past events and actions.
- Use probing questions to gain deeper insights into the candidate’s behavior.
- Analysis:
- Evaluate responses against the defined competencies.
- Look for patterns and consistency in behavior.
Importance of Competency Mapping in BEI
Competency mapping is crucial in the BEI process. It involves identifying the key skills, behaviors, and attitudes required for the role and ensuring the interview questions are aligned to assess these competencies effectively.
Characteristics of Behavioral Event Interviewing
1. Real and Not Hypothetical
BEI questions are based on real past events rather than hypothetical situations. This ensures that candidates provide concrete examples of how they have behaved in actual work scenarios, offering more reliable insights into their capabilities.
2. Based on the Past
The core of BEI is its focus on past behavior. By examining what candidates have done in previous roles, interviewers can better predict how they will perform in similar situations in the future. This historical perspective provides a solid foundation for evaluating competencies.
3. Involves Funneling by Probing Deeper
BEI uses a funneling technique, where interviewers start with broad questions and then probe deeper into the specifics. For instance, an interviewer might ask about a general project the candidate managed and then follow up with detailed questions about their decision-making process, challenges faced, and outcomes achieved. This helps uncover deeper insights into the candidate’s thought processes and behaviors.
4. Asks Open-Ended Questions
BEI relies heavily on open-ended questions that encourage candidates to elaborate on their experiences. Examples include “Can you describe a time when you had to manage a difficult team member?” or “Tell me about a situation where you had to adapt quickly to changes.” These questions allow candidates to provide detailed responses that reveal their competencies and problem-solving abilities.
How BEI Questions Differ from Other Types of Questions
Hypothetical Questions
Hypothetical questions ask candidates to describe how they would handle a future situation, often starting with “What would you do if…?” While these questions can provide some insight into a candidate’s thought process, they often lead to idealized or rehearsed answers that may not reflect actual behavior.
Generic Questions
Generic questions are broad and often do not delve into specifics, such as “Tell me about yourself” or “What are your strengths and weaknesses?” These questions can result in vague responses that do not provide a clear picture of the candidate’s competencies or fit for the role.
Knowledge Check Questions
Knowledge check questions test a candidate’s theoretical or technical knowledge, such as “What is the capital of France?” or “Explain the concept of Object-Oriented Programming.” While these are useful for assessing specific knowledge, they do not evaluate how a candidate applies this knowledge in real-world situations.
Behavioral Event Interview Questions
In contrast, BEI questions are designed to elicit detailed responses about past behaviors and actions in specific situations, such as “Describe a time when you had to lead a team through a challenging project. What was the outcome?” These questions provide insights into how candidates have actually performed in the past, offering a more reliable predictor of future behavior and performance.
Benefits of Behavioral Event Interviewing
Advantages Over Traditional Interviewing Techniques
Behavioral Event Interviewing offers several advantages over traditional interviewing techniques:
- Predictive Accuracy: BEI provides a more accurate prediction of a candidate’s future performance.
- Objective Evaluation: The structured nature of BEI reduces biases and ensures a fair evaluation process.
- Deep Insights: By focusing on past behavior, BEI uncovers the true competencies and motivations of candidates.
Real-World Examples and Success Stories
Many organizations have successfully implemented BEI to enhance their hiring processes. For instance:
- Google: Known for its rigorous hiring processes, Google employs BEI to identify candidates who possess the necessary competencies for their roles. This approach has helped Google maintain a high standard of talent across its diverse teams.
- Walmart: As one of the largest employers in the world, Walmart uses BEI to ensure they hire employees who can thrive in a fast-paced retail environment. This method helps Walmart select candidates who demonstrate the ability to handle various customer service scenarios effectively.
- Amazon: Amazon uses BEI to evaluate candidates based on their ability to innovate and manage large-scale operations. By focusing on past behaviors, Amazon ensures that new hires align with its leadership principles and customer-centric culture.
- Microsoft: Microsoft employs BEI to assess technical and soft skills, ensuring a balanced evaluation that aligns with the company’s values and objectives. This approach has been integral to Microsoft’s success in maintaining a dynamic and innovative workforce.
Using the STAR Method in BEI
The STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) is a useful framework for extracting detailed responses during a BEI. Here’s an example to illustrate this:
Example Question: “Describe a time when you had to manage a project with a tight deadline.”
- Situation: In my previous job at XYZ Corp, we had a major product launch scheduled, but our development team fell behind schedule.
- Task: As the project manager, it was my responsibility to ensure that the product was ready on time for the launch.
- Action: I organized daily stand-up meetings to monitor progress, reallocated resources to critical tasks, and negotiated with stakeholders to prioritize essential features.
- Result: We managed to launch the product on time, which resulted in a 20% increase in sales for the quarter and positive feedback from our customers.
By using the STAR method, interviewers can gain a clear and structured understanding of the candidate’s past behavior and achievements.
Tips for Evaluating Candidate Responses
- Look for Specifics: Ensure the candidate provides specific examples rather than general statements.
- Assess Impact: Evaluate the impact of the candidate’s actions on the outcome.
- Behavior Consistency: Check for consistency in behavior across different situations.
Training for Behavioral Event Interviews
Importance of Training Interviewers
Proper training for interviewers is essential to ensure the effectiveness of BEI. Trained interviewers can better identify relevant behaviors and competencies, leading to more accurate evaluations.
Best Practices for BEI Training Programs
- Comprehensive Workshops: Conduct workshops that cover all aspects of BEI.
- Role-Playing: Use role-playing exercises to practice interviewing techniques.
- Continuous Learning: Provide ongoing training and support to keep interviewers updated on best practices.
Importance of Documenting Evidence in BEI
Systematic Documentation
Documenting evidence during BEI is crucial for maintaining a consistent and objective evaluation process. Detailed notes help capture key points from the interview, ensuring that important information is not forgotten during reviews or debriefs.
Support for Decision Making
Well-documented evidence provides a solid foundation for decision making. It allows hiring managers to compare candidates based on concrete examples of past behavior, reducing the influence of subjective opinions.
Legal and Compliance Reasons
Accurate documentation can also protect the organization from potential legal issues. Having a clear record of the interview process and the rationale behind hiring decisions can be invaluable in defending against discrimination claims or other legal challenges.
Implementing a BEI Framework
Key Components of an Effective BEI Framework
- Competency Model: Develop a clear competency model tailored to the organization’s needs.
- Structured Interview Guide: Create a structured interview guide with predefined questions.
- Evaluation Criteria: Establish clear evaluation criteria to assess candidate responses.
How to Integrate BEI into Existing Hiring Processes
Integrating BEI into existing hiring processes involves:
- Stakeholder Buy-In: Gain support from key stakeholders within the organization.
- Pilot Programs: Start with pilot programs to refine the process.
- Feedback Loop: Implement a feedback loop to continuously improve the BEI process.
Challenges and Solutions in BEI
Common Challenges Faced During BEI
- Resistance to Change: Some interviewers may resist adopting a new method.
- Time-Consuming: BEI can be more time-consuming than traditional interviews.
- Subjectivity: Despite its structured nature, some level of subjectivity can remain.
Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
- Change Management: Implement change management strategies to ease the transition.
- Efficiency Improvements: Streamline the BEI process to reduce time requirements.
- Standardization: Standardize the evaluation criteria to minimize subjectivity.
Strategies for Conducting an Effective BEI (Behavioral Event Interviewing).
Conclusion
Behavioral Event Interviewing stands out as a powerful tool in the modern recruiter’s toolkit. By focusing on past behaviors and aligning them with required competencies, BEI offers a predictive and objective approach to hiring. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of talent acquisition in 2024, adopting and mastering BEI can significantly enhance the quality of hires and drive organizational success.





